Pruning and trimming are essential techniques every gardener should learn to keep plants healthy and thriving. Whether you’re working with indoor houseplants or an outdoor garden, understanding how to prune and trim plants for healthy growth can make the difference between a struggling plant and a flourishing one. This guide will walk you through the methods, tools, and timing you need to ensure your plants grow strong and beautiful.
Why Pruning and Trimming Matter
Trimming and pruning are more than just aesthetic practices—they directly impact plant health. When done correctly, they can:
- Encourage new growth
- Improve air circulation
- Prevent disease
- Maintain shape and size
- Promote flowering or fruiting
Ignoring pruning can lead to overgrowth, poor light penetration, and vulnerability to pests.
Tools You’ll Need
Before you begin, gather the proper tools:
- Pruning shears (for thin stems)
- Loppers (for thicker branches)
- Scissors (for delicate houseplants)
- Gardening gloves
- Rubbing alcohol (to disinfect tools)
- A small rake or broom (for cleanup)
Always ensure your tools are sharp and clean to avoid damaging plant tissue or spreading disease.
When to Prune and Trim Plants
Timing depends on the type of plant:
- Spring: Ideal for most flowering shrubs and perennials.
- Summer: Good for shaping fast-growing plants.
- Fall: Light trimming; avoid heavy cuts as plants prepare for dormancy.
- Winter: Best for deciduous trees and dormant plants.
Avoid pruning when a plant is under stress from heat, cold, or disease.
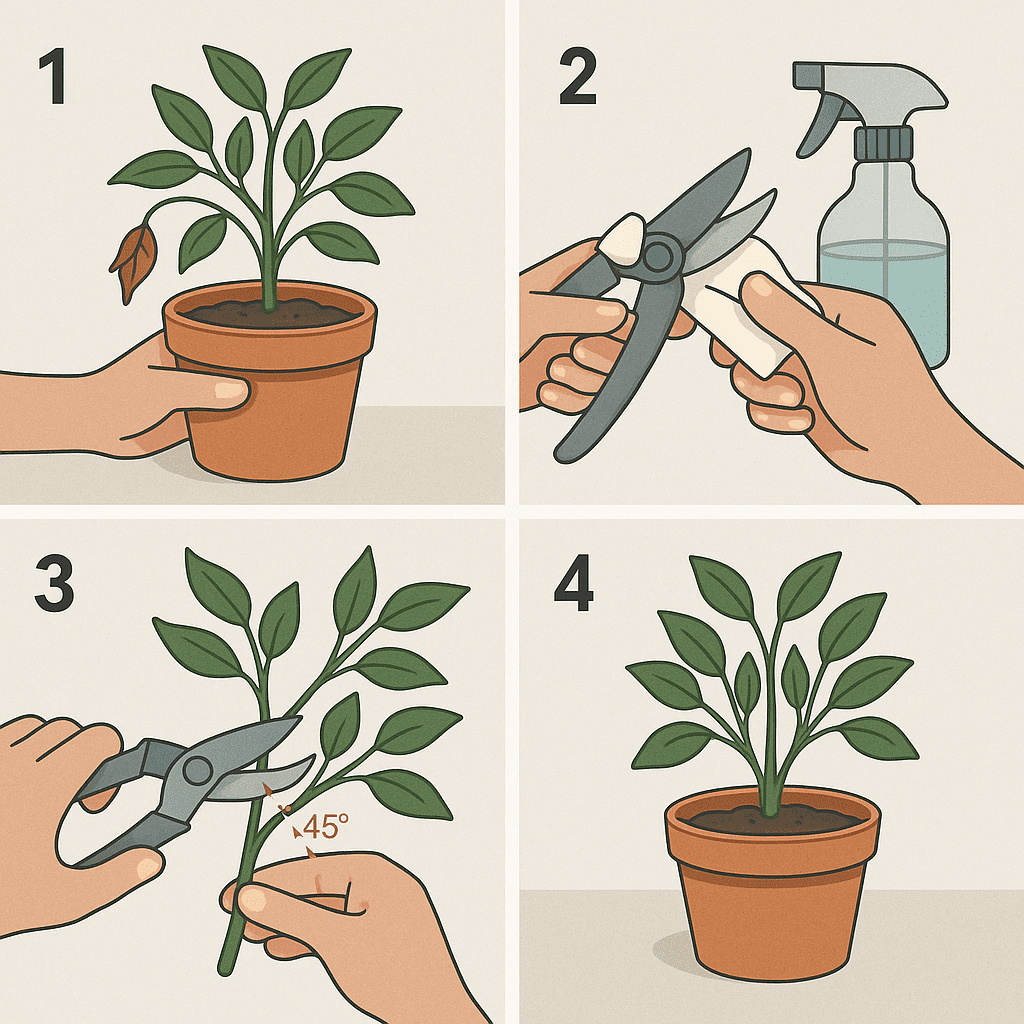
Step-by-Step: How to Prune and Trim Your Plants
Step 1: Identify What Needs Trimming
Start by inspecting the plant and removing:
- Dead or brown leaves
- Yellowing or diseased branches
- Overlapping branches causing congestion
- Leggy stems with few leaves
Step 2: Disinfect Your Tools
Wipe blades with rubbing alcohol before and after pruning each plant. This prevents the spread of bacteria or fungus.
Step 3: Make Clean, Angled Cuts
Always cut at a 45-degree angle just above a leaf node or bud. This encourages new growth and prevents water from pooling on the cut.
Step 4: Shape the Plant
Trim evenly to give the plant a symmetrical, natural shape. Remove up to 25% of the total foliage in one session to avoid stress.
Step 5: Remove Suckers and Water Sprouts
For trees and shrubs, remove unwanted growth at the base (suckers) and fast-growing vertical stems (water sprouts) that sap energy.
Tips for Specific Plant Types
Houseplants
- Pinch back leggy stems to encourage bushiness.
- Trim yellow leaves close to the base.
- Avoid cutting more than one-third of the plant at once.
Herbs
- Harvest regularly to keep them from flowering.
- Cut above a leaf pair to promote branching.
- Basil, mint, and parsley respond well to frequent pruning.
Flowering Plants
- Deadhead spent blooms to encourage more flowers.
- Prune after flowering to avoid cutting off next season’s buds.
Fruit Trees
- Prune in winter when dormant.
- Open up the center for better light and air circulation.
- Remove competing branches to create a strong structure.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Over-pruning: Removes too much foliage, stressing the plant.
- Cutting at the wrong spot: Damages the plant or inhibits growth.
- Using dull or dirty tools: Spreads disease or causes jagged cuts.
- Pruning at the wrong time: Can reduce blooms or stunt growth.
Benefits of Regular Pruning
- Improved plant vigor
- Increased yield (for fruiting plants)
- Enhanced shape and structure
- Better resistance to pests and diseases
- Healthier, longer-lasting plants
Sustainable Gardening Tip
Instead of tossing trimmed foliage, compost it! Pruned material can enrich your garden soil if properly processed in a compost bin.
Need high-quality pruning tools? Visit Gardener’s Supply Company for eco-friendly, durable gardening equipment.
For more sustainable ideas, read our guide on Hanging Planters with Old Bottles.
Conclusion: A Simple Habit That Pays Off
Learning how to prune and trim plants for healthy growth is a foundational skill in gardening. With the right tools, timing, and techniques, you can dramatically improve the health and appearance of your plants. Start small, observe your plants closely, and enjoy the satisfaction of vibrant, well-maintained greenery.
Save this guide for your next pruning day—or share it with a fellow plant lover who needs a little trimming confidence!
FAQ: Plant Pruning and Trimming
Q1: How often should I prune my plants?
Most houseplants benefit from light trimming every few weeks, while trees and shrubs may only need seasonal pruning.
Q2: Can I prune plants during flowering?
Avoid pruning while plants are actively blooming unless removing dead or spent flowers. For major cuts, wait until after flowering.
Q3: What should I do with trimmed parts?
Healthy trimmings can be composted. Avoid composting diseased or infested clippings.
Written by Kate Smith | Plant Care Enthusiast & Urban Gardener
